Estate Diamond Value Guide
The Estate Diamond Value Guide starts with the one gemstone that
enjoys the greatest demand in the world... diamond.
The method for calculating the Cash Value for diamond is
quite complex. However, you can use this estate
jewelry value guide to estimate the Cash Value with the
following information. Let me remind you that this
estate jewelry value guide is a reference and it is best
to have a GIA Graduate Gemologist Appraiser examine any
jewelry or fine watch to get an accurate and current Cash
Market Value. So let's get to it...
Small side diamonds (under 0.20 carat) are referred to as “melee”. These small diamonds are divided into numerous cutting styles and most have the same 58 facets as a modern round brilliant cut main diamonds. The Cash Value of melee diamonds is based on weight and quality, but because they are small their weight is low and so is the Cash Value. Whether round, square or other shape, melee diamonds have a cash value which is in the $25 - $500 per carat range. A typical melee diamond (or accent diamond) may weigh 0.02ct which would give a value between $0.50 and $10 each. Of course larger fine melee diamonds are worth considerably more. Colored melee gemstones like ruby, sapphire or emerald have a lower value (compared to diamonds) plus colored gemstones can be difficult to remove without breaking. So to sum it up if a diamond ring has a total side diamond weight of 1/2 carat (0.50ct) of very good quality the cash market value of those side diamonds would be in the $150 range ($300 x 0.50). We would still need to add the precious metal value and the center stone value, see below.
Small side diamonds (under 0.20 carat) are referred to as “melee”. These small diamonds are divided into numerous cutting styles and most have the same 58 facets as a modern round brilliant cut main diamonds. The Cash Value of melee diamonds is based on weight and quality, but because they are small their weight is low and so is the Cash Value. Whether round, square or other shape, melee diamonds have a cash value which is in the $25 - $500 per carat range. A typical melee diamond (or accent diamond) may weigh 0.02ct which would give a value between $0.50 and $10 each. Of course larger fine melee diamonds are worth considerably more. Colored melee gemstones like ruby, sapphire or emerald have a lower value (compared to diamonds) plus colored gemstones can be difficult to remove without breaking. So to sum it up if a diamond ring has a total side diamond weight of 1/2 carat (0.50ct) of very good quality the cash market value of those side diamonds would be in the $150 range ($300 x 0.50). We would still need to add the precious metal value and the center stone value, see below.
The Diamond 4 C’s is the key to Cash
Value: Color, Clarity, Cut and Carat weight
Color: The
first step in grading a diamond is color. Continue
reading this part of our estate jewelry value guide to
learn more. The color grade of a diamond refers to
how closely its body color approaches complete
colorlessness. Color has nothing to do with the amount of
brilliance (sparkle). The best color for a diamond is in
fact an absence of any color, colorless. A truly colorless
stone (D color) will carry a premium price, and the larger
that diamond, the greater the premium per carat.
Most diamonds have a trace of yellow, brown, or gray body
color. Though a lot of diamonds will appear to be
colorless, most actually possess subtle shade differences.
These variances in color are due to traces of elements
such as nitrogen and boron that become assimilated into a
diamond's atomic structure during the original formation.
Most commonly, a diamond will have a hint of yellow or
brown due to traces of nitrogen. This "hint of
color" is viewed, and then graded, from the side position
in a matte white card under color corrected lights by a
trained gemologist. Each color grade is it's own
single grade (F color), however, below are the classes of
color.
D-E-F: Colorless
G-H-I: Near colorless; looks nearly colorless when mounted
J-K-L-M: Faint yellow, grey or brown, face up
N-O-P-Q: Very light yellow, grey or brown to obvious color
RSTUVWXYZ: Increasingly darker face up color
Clarity: Clarity describes the purity of a diamond. This is determined by the number, size, nature, and location of the internal (inclusions) and external (blemishes) imperfections. Nitrogen and other elements trapped within a stone during its formation effect the ultimate color, and minerals embedded in a diamond during crystallization will influence the diamond’s clarity. The fewer the inclusions the more rare and precious the stone will be. The number, color, size, and position of any inclusions will specify a diamond's clarity. If the diamond does not have a GIA diamond certificate (report) to establish a diamond's clarity, it must be examined by a GIA Graduate Gemologist under a 10x magnification; the fewer the inclusions, the more valuable the diamond will be.
Two methods used to enhance the clarity grade given to a diamond are laser drilling and fracture filling. Laser drilling is the process in which a laser is used to drill a microscopic hole into a diamond and then treated to remove the included material. The second treatment is fracture filling. This method involves using heat and pressure to impregnate an open fracture, filling it and making the fracture less visible. Treated diamonds have a significant drop in Cash Market Value. Blemishes are abrasions such scratches, pits or nicks on caused by wear or coming in contact with other diamonds. Extra Facets are small facets placed to remove imperfections; not part of the cutting style.
D-E-F: Colorless
G-H-I: Near colorless; looks nearly colorless when mounted
J-K-L-M: Faint yellow, grey or brown, face up
N-O-P-Q: Very light yellow, grey or brown to obvious color
RSTUVWXYZ: Increasingly darker face up color
Clarity: Clarity describes the purity of a diamond. This is determined by the number, size, nature, and location of the internal (inclusions) and external (blemishes) imperfections. Nitrogen and other elements trapped within a stone during its formation effect the ultimate color, and minerals embedded in a diamond during crystallization will influence the diamond’s clarity. The fewer the inclusions the more rare and precious the stone will be. The number, color, size, and position of any inclusions will specify a diamond's clarity. If the diamond does not have a GIA diamond certificate (report) to establish a diamond's clarity, it must be examined by a GIA Graduate Gemologist under a 10x magnification; the fewer the inclusions, the more valuable the diamond will be.
Two methods used to enhance the clarity grade given to a diamond are laser drilling and fracture filling. Laser drilling is the process in which a laser is used to drill a microscopic hole into a diamond and then treated to remove the included material. The second treatment is fracture filling. This method involves using heat and pressure to impregnate an open fracture, filling it and making the fracture less visible. Treated diamonds have a significant drop in Cash Market Value. Blemishes are abrasions such scratches, pits or nicks on caused by wear or coming in contact with other diamonds. Extra Facets are small facets placed to remove imperfections; not part of the cutting style.
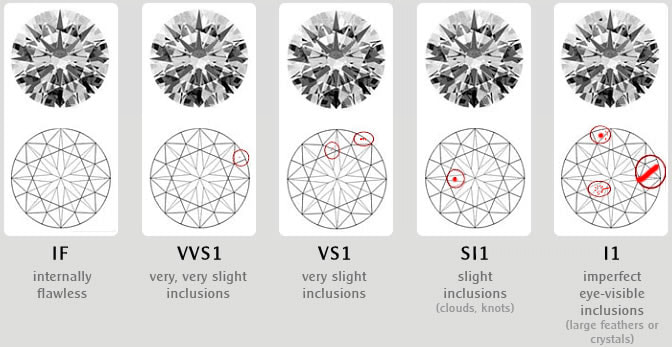
IF - Internally Flawless No inclusions visible at 10x
magnification.
VVS1 - Very Very Slightly Included #1 Inclusions that are extremely difficult to detect at 10x.
VVS2 - Very Very Slightly Included #2 Inclusions that are very difficult to detect at 10x.
VS1 - Very Slightly Included #1 Minor inclusions, difficult to detect at 10x.
VS2 - Very Slightly Included #2 Minor inclusions, somewhat difficult to detect at 10x.
SI1 - Slightly Included #1 Noticeable inclusions, easy to detect at 10x.
SI2 - Slightly Included #2 Noticeable inclusions, very easy to detect at 10x.
I1 - Included #1 Obvious inclusions. Can detect with the unaided eye. Possible durability issues.
I2 - Included #2 Obvious inclusions. Easy to see with the unaided eye. Durability issues/cloudy.
I3 - Included #3 Obvious inclusions. Very easy to see with the unaided eye. Not for good jewelry.
The above clarity grading grades are in accordance with the GIA (Gemological Institute of America). Clarity can be subjective so it is very good if you already have a GIA diamond grading certificate (report). Most jewelers are not GIA Graduate Gemologists. When liquidating diamonds it is very important to make sure that a GIA Graduate Gemologist examines your diamonds so you are sure to get the full value.
VVS1 - Very Very Slightly Included #1 Inclusions that are extremely difficult to detect at 10x.
VVS2 - Very Very Slightly Included #2 Inclusions that are very difficult to detect at 10x.
VS1 - Very Slightly Included #1 Minor inclusions, difficult to detect at 10x.
VS2 - Very Slightly Included #2 Minor inclusions, somewhat difficult to detect at 10x.
SI1 - Slightly Included #1 Noticeable inclusions, easy to detect at 10x.
SI2 - Slightly Included #2 Noticeable inclusions, very easy to detect at 10x.
I1 - Included #1 Obvious inclusions. Can detect with the unaided eye. Possible durability issues.
I2 - Included #2 Obvious inclusions. Easy to see with the unaided eye. Durability issues/cloudy.
I3 - Included #3 Obvious inclusions. Very easy to see with the unaided eye. Not for good jewelry.
The above clarity grading grades are in accordance with the GIA (Gemological Institute of America). Clarity can be subjective so it is very good if you already have a GIA diamond grading certificate (report). Most jewelers are not GIA Graduate Gemologists. When liquidating diamonds it is very important to make sure that a GIA Graduate Gemologist examines your diamonds so you are sure to get the full value.
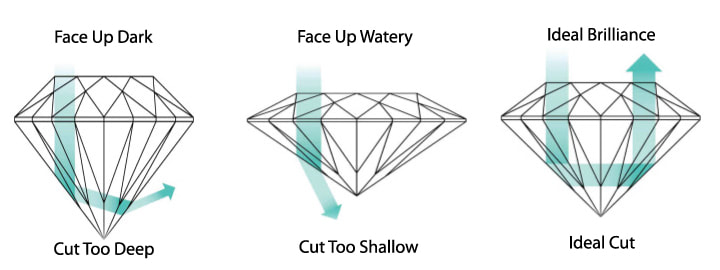
Cut:
(proportions): Cut is used to describe how closely the
proportions of a brilliant cut diamond are to ideal
proportions. A diamond with deep proportions will not only
look smaller when set but will look less brilliant than an
ideal cut diamond.
A diamond with a shallow cut will look bigger however it will also appear watery (less sparkle). A diamond with a deep cut will not only appear smaller but will look dark. Ideal Proportions will result in a diamond having maximum brilliance which is more in demand and brings a premium. A diamond cut to Ideal Proportions loses more of the rough diamond material when cutting and it requires a more skilled diamond cutter thus increasing the price per carat. Round diamond are worth more “per carat” than fancy shaped diamonds. The reason is that round diamonds are the most brilliant cut and typically more rough diamond material is ground away when cutting a round diamond versus other shapes. Well cut fancy shaped diamonds like Oval, Pear, Marquise, Princess, Emerald cut, Asscher and Cushion shapes still enjoy very good to high Cash Market Values.
A diamond with a shallow cut will look bigger however it will also appear watery (less sparkle). A diamond with a deep cut will not only appear smaller but will look dark. Ideal Proportions will result in a diamond having maximum brilliance which is more in demand and brings a premium. A diamond cut to Ideal Proportions loses more of the rough diamond material when cutting and it requires a more skilled diamond cutter thus increasing the price per carat. Round diamond are worth more “per carat” than fancy shaped diamonds. The reason is that round diamonds are the most brilliant cut and typically more rough diamond material is ground away when cutting a round diamond versus other shapes. Well cut fancy shaped diamonds like Oval, Pear, Marquise, Princess, Emerald cut, Asscher and Cushion shapes still enjoy very good to high Cash Market Values.
Carat weight: Diamond weight is weight, not size. Diamond weight
is stated in carats and may be described in decimal or
fractional parts of a carat. If the weight is given in
decimal parts of a carat, the figure should be accurate to
the last decimal place. For example, ”0.30
carat” could represent a diamond that weighs between
.295 and .304 carat. Some retailers describe diamond
weight in fractions, using the fraction to represent a
range of weights. A diamond described as 1/2 carat should
weigh between .47 and .54 carat. Value per carat increases
with carat size, because larger rough diamonds occur
less frequently. In other words, two half-carat diamonds
taken together will not cost as much as 1, one-carat
diamond, as the one-carat stone is more rare. Also, a
premium is added to diamond prices as they exceed each
½ carat increment in weight. So a 2.50 carat
diamond is worth more “per carat” than a 2.00
carat diamond.
Cash Value: So how much will I get for my $10,000 diamond ring? That answer varies significantly as it depends on many factors like when you bought it, what the quality is and who appraised it. For example a 1.50 carat round diamond of very good quality bought in the 70’s and appraised at $8,000 may have a Cash Market Value of $10,000. Whereas a fair quality 1.50 carat pear shaped diamond bought last year and appraised at $15,000 may have Cash Market Value of $5,000. The unfortunate fact is that jewelry appraisers are often biased towards their own merchandise and there are no laws governing jewelry appraisal prices.
Additionally, most jewelers are not gemologists. Since their grading skill is lacking they typically grade lower when buying to make sure they do not make a mistake. That is why it is important to only have a GIA Graduate Gemologist examine your jewelry. GIA (Gemological Institute of America) is the one and only world recognized diamond grading laboratory. There are numerous other gemstones labs that issue grading reports, but none have the accuracy or carry the prominence of the GIA.
A vital point to understand about a Retail Appraisal Price is that it is used for insurance purposes… to replace the item at full retail price in a retail store in the case of a loss.
The Retail Appraisal Price cannot be confused with the Cash Market Value. The Cash Market Value takes only the precious metal value, plus the gemstone value, plus any bonus value (for very special or signed jewelry pieces). We already covered the precious metal Cash Values, and below you will find a very general list of diamond cash values. There are also natural colored diamonds, and in the case of case of blue, green, pink, orange and red diamonds the value can be much, much higher than white diamonds. Fancy natural brown, grey or black diamonds usually have a price lower than white diamonds of equal size and quality.
Size Shape Quality Cash Value Range
0.75ct Round Very Good - Exc $900 - $2,200
0.75ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $700 - $1,800
1.00ct Round Very Good - Exc $3,500 - $7,000
1.00ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $2,800 - $5,000
2.00ct Round Very Good - Exc $12,000 - $25,000
2.00ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $ 9,000 - $17,000
5.00ct Round Very Good - Exc $60,000 – 205,000
5.00ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $50,000 – 175,000
The above ranges represent Cash Market Values for diamonds with very good color (F-H), very good clarity (VS – SI) and excellent proportions. There are other factors like fluorescence, condition and specific proportions which can lower or raise prices. Higher quality (D,E,F color / IF – VVS clarity) diamonds will have a significantly higher Cash Market Values. Conversely, lower quality diamonds will have lower cash market values. But at least you now have a cash market value range that will cover most very good quality diamonds that are set in jewelry. Looking for a Gold & Diamond Buyer, click here.
Fancy shaped diamonds like Pear shaped, Oval shaped, Heart shaped, Marquise shaped, Emerald cut, Asscher cut, Cushion cut and other shapes sell on the market for lower prices than rounds. Fancy shaped diamonds will not achieve the maximum brilliance that a round shape can and fancy shaped diamonds are in lower demand. They cost less than rounds when bought, and have a lower cash market value versus rounds when being liquidated. That being said, well cut fancy shaped diamonds are wonderful and always enjoy high cash market values.
Cash Value: So how much will I get for my $10,000 diamond ring? That answer varies significantly as it depends on many factors like when you bought it, what the quality is and who appraised it. For example a 1.50 carat round diamond of very good quality bought in the 70’s and appraised at $8,000 may have a Cash Market Value of $10,000. Whereas a fair quality 1.50 carat pear shaped diamond bought last year and appraised at $15,000 may have Cash Market Value of $5,000. The unfortunate fact is that jewelry appraisers are often biased towards their own merchandise and there are no laws governing jewelry appraisal prices.
Additionally, most jewelers are not gemologists. Since their grading skill is lacking they typically grade lower when buying to make sure they do not make a mistake. That is why it is important to only have a GIA Graduate Gemologist examine your jewelry. GIA (Gemological Institute of America) is the one and only world recognized diamond grading laboratory. There are numerous other gemstones labs that issue grading reports, but none have the accuracy or carry the prominence of the GIA.
A vital point to understand about a Retail Appraisal Price is that it is used for insurance purposes… to replace the item at full retail price in a retail store in the case of a loss.
The Retail Appraisal Price cannot be confused with the Cash Market Value. The Cash Market Value takes only the precious metal value, plus the gemstone value, plus any bonus value (for very special or signed jewelry pieces). We already covered the precious metal Cash Values, and below you will find a very general list of diamond cash values. There are also natural colored diamonds, and in the case of case of blue, green, pink, orange and red diamonds the value can be much, much higher than white diamonds. Fancy natural brown, grey or black diamonds usually have a price lower than white diamonds of equal size and quality.
Size Shape Quality Cash Value Range
0.75ct Round Very Good - Exc $900 - $2,200
0.75ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $700 - $1,800
1.00ct Round Very Good - Exc $3,500 - $7,000
1.00ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $2,800 - $5,000
2.00ct Round Very Good - Exc $12,000 - $25,000
2.00ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $ 9,000 - $17,000
5.00ct Round Very Good - Exc $60,000 – 205,000
5.00ct Fancy Very Good - Exc $50,000 – 175,000
The above ranges represent Cash Market Values for diamonds with very good color (F-H), very good clarity (VS – SI) and excellent proportions. There are other factors like fluorescence, condition and specific proportions which can lower or raise prices. Higher quality (D,E,F color / IF – VVS clarity) diamonds will have a significantly higher Cash Market Values. Conversely, lower quality diamonds will have lower cash market values. But at least you now have a cash market value range that will cover most very good quality diamonds that are set in jewelry. Looking for a Gold & Diamond Buyer, click here.
Fancy shaped diamonds like Pear shaped, Oval shaped, Heart shaped, Marquise shaped, Emerald cut, Asscher cut, Cushion cut and other shapes sell on the market for lower prices than rounds. Fancy shaped diamonds will not achieve the maximum brilliance that a round shape can and fancy shaped diamonds are in lower demand. They cost less than rounds when bought, and have a lower cash market value versus rounds when being liquidated. That being said, well cut fancy shaped diamonds are wonderful and always enjoy high cash market values.
Click buttons below for the Estate & Gold Jewelry Guide sections.
The best way to contact us is to CLICK HERE and tell us about your items for sale, or ask us a question.
Free email consultation. It is always our goal to offer complete settlement within 1 business day of
our agreement via bank wire or paper check, your choice.
Are you ready to contact our Large Diamond
Buyer? Simply Click Here to contact us.
I will personally make sure you experience a safe, fair and confidential transaction. Thank you.
Privacy Policy
gemwin.com is a buyer of large diamonds of all shapes and qualities. We are not endorsed nor affiliated with The G.I.A. (Gemological Institute of America) CLICK HERE for GIA's website. We are not endorsed nor affiliated with E.G.L. (European Gemological Lab) CLICK HERE for EGL's website. We are not endorsed nor affiliated with AGS (American Gem Society) CLICK HERE for the AGS website.
I will personally make sure you experience a safe, fair and confidential transaction. Thank you.
Privacy Policy
gemwin.com is a buyer of large diamonds of all shapes and qualities. We are not endorsed nor affiliated with The G.I.A. (Gemological Institute of America) CLICK HERE for GIA's website. We are not endorsed nor affiliated with E.G.L. (European Gemological Lab) CLICK HERE for EGL's website. We are not endorsed nor affiliated with AGS (American Gem Society) CLICK HERE for the AGS website.
Copyright 2006 - 2023